What is a three-phase transformer?
A three-phase transformer is a power transformer. It has three independent isometric secondary coils and a shared primary and secondary coil for converting a three-phase alternating current of high voltage and low current into a three-phase alternating current of low voltage and high current or the reverse conversion.
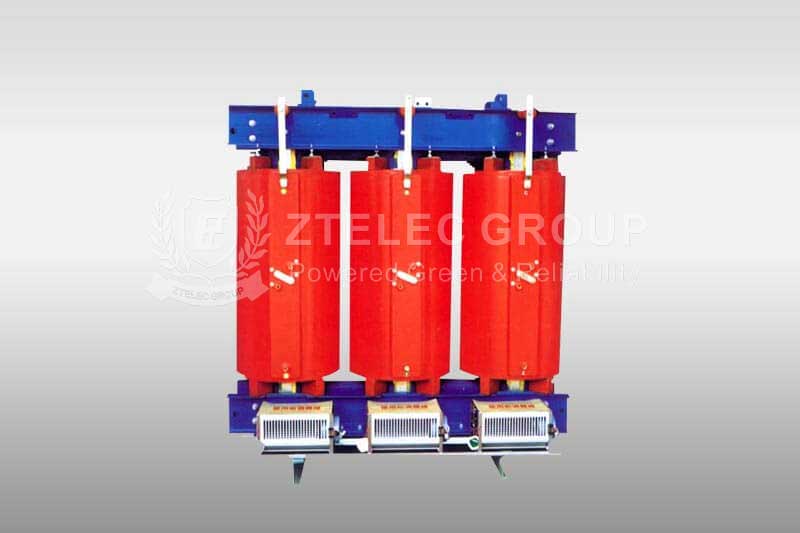

How does a three-phase transformer work?
The operation of all types of transformers is subject to Faraday's law of induction – it states that the magnitude of the emf induced within a circuit is directly proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux cutting across the circuit.
Therefore, a conductor placed near a changing magnetic field – from an AC-powered electromagnet, for instance – will have an electric current. Electromagnetic circuits of this nature are called primary windings.
As the electric current collapses and is generated continually at a particular frequency, the magnetic field collapses and recreates similarly. This alternating magnetic field induces a current in the conductors cut by this flux; they are then called secondary windings. The frequency is the same across both windings.
What is the type of three-phase transformer?
Core-type Transformer: All three limb cores are assembled together in an interesting magnetic circuit with primary and secondary windings wound on them. This type is preferred for higher power ratings.
Shell-type Transformer: In this, the primary and secondary windings of the three single phase transformer units are placed in separate limb cores inside a steel shell structure. This type is used in lower power ratings.
What is the composition of three-phase transformer?
Three-phase transformer consists of core, winding and insulating oil.
1.The core is the basic support structure of the transformer, which is made of highly magnetic conductive materials to conduct the magnetic field and improve the efficiency of energy transmission.2.The winding is the current conductor of the transformer, which is divided into primary winding and secondary winding, and realizes energy transmission through the induction of current.
3.The insulating oil plays the role of insulation and cooling to ensure the normal operation of the transformer.
In addition, three-phase transformers also include thermometers, pressure relief systems, coolers, tanks, voltage regulators and other important components.
What is the purpose of the three-phase transformer?
First, three-phase transformers are mainly used in power transmission and distribution systems. In power systems, transformers are responsible for converting high-voltage electrical energy into low-voltage electrical energy suitable for various applications. Through power transmission lines, high-voltage electrical energy is transmitted from the power station to the substation, and is reduced by three-phase transformers, making it suitable for low-voltage electrical energy for use in factories, commercial buildings and homes. In this way, we can easily use electricity to drive various equipment and lighting systems.
Second, three-phase transformers also play an important role in industrial production. Many industrial equipment and machines require the use of high voltages to operate, and these voltages can pose a threat to personal safety. By using three-phase transformers, we can convert high voltages into safe and suitable voltages to ensure a safe working environment. For example, in the welding shop, three-phase transformers are used to provide the appropriate voltage and current to meet the requirements of the welding equipment.








Leave A Comment